Introduction
Consumer price inflation is a critical economic indicator that reflects the rate at which the prices of goods and services in an economy increase over a specific period. In November 2024, the UK’s inflation figures have drawn significant attention, given the ongoing challenges in the global economy, post-Brexit adjustments, and fluctuating energy prices. This article provides a detailed analysis of the UK’s consumer price inflation data for November 2024, its contributing factors, and the implications for businesses and households.
Key Highlights of UK Inflation Data for November 2024
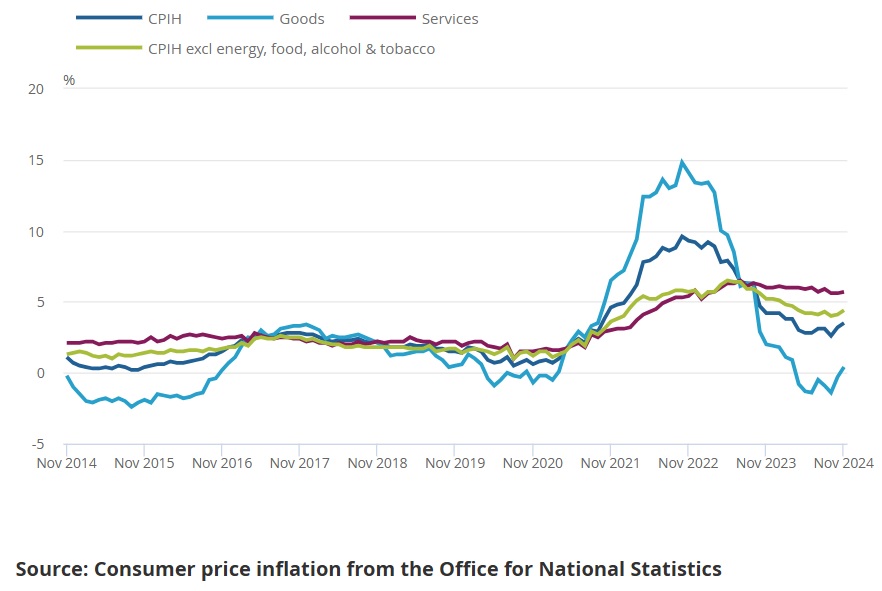
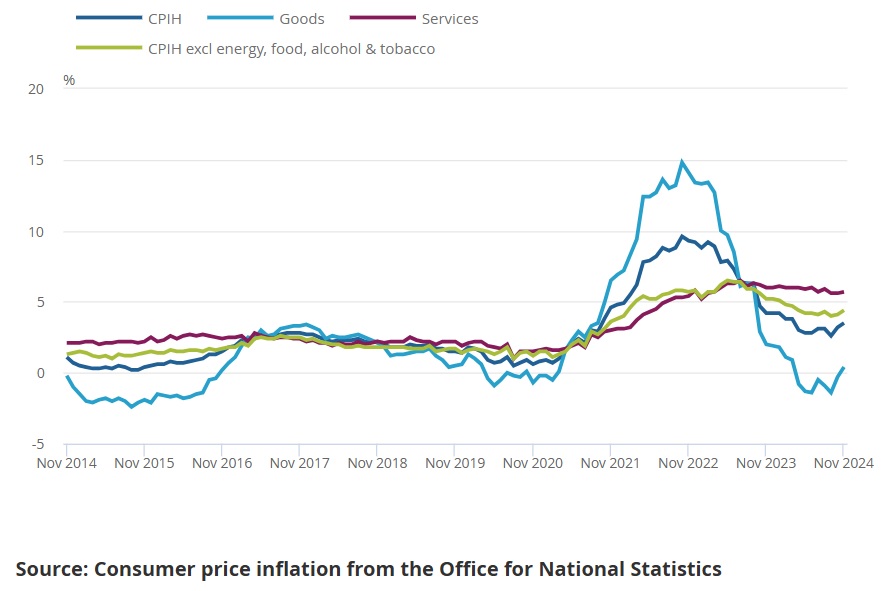
- Overall Inflation Rate: The Consumer Prices Index (CPI) rose by 4.2% year-on-year in November 2024, slightly lower than the 4.5% recorded in October.
- Core Inflation: Excluding volatile items such as energy and food, core inflation stood at 3.6%, indicating persistent underlying inflationary pressures.
- Monthly Change: Prices increased by 0.3% between October and November 2024.
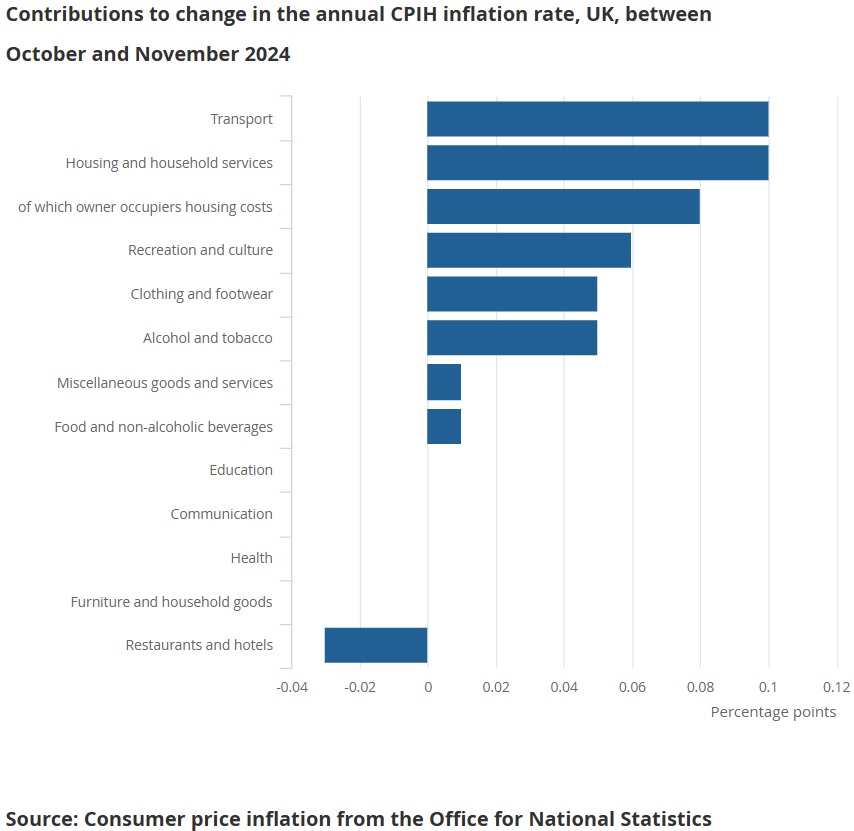
- Contributing Sectors:
- Energy and Fuel: Despite declining global oil prices, household energy bills remained elevated due to delays in regulatory price adjustments.
- Food and Non-Alcoholic Beverages: Food prices surged by 6.1% year-on-year, driven by supply chain issues and rising agricultural costs.
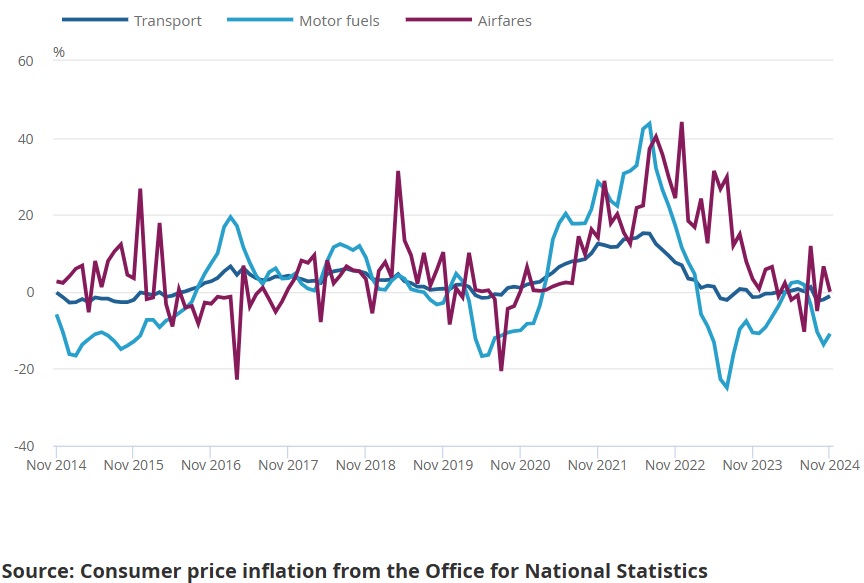
- Services: Services inflation was reported at 3.8%, reflecting higher wages and increased costs in hospitality and transport sectors.
Analysis of Inflation Trends
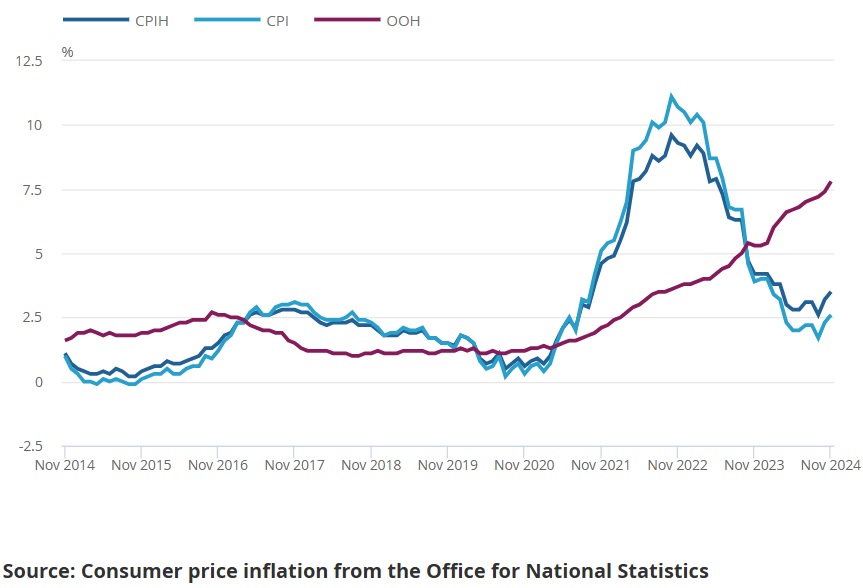
- Energy Prices: Energy prices have been a dominant driver of UK inflation throughout 2024. While crude oil prices fell below $70 per barrel in November, the delayed pass-through to consumer energy bills kept inflation in this category high. The Ofgem price cap adjustments expected in early 2025 might provide relief to households.
- Food Inflation: Persistent food inflation reflects global disruptions in grain supplies, partly due to geopolitical tensions and extreme weather events affecting crop yields. Additionally, labor shortages in the UK’s agricultural and logistics sectors have added to cost pressures.
- Core Inflation Stability: The relatively stable core inflation at 3.6% indicates resilience in demand for services and consumer goods. Wage growth in sectors like healthcare and education has contributed to sustained spending power, counterbalancing the effects of rising interest rates.
Government and Bank of England Responses
- Interest Rates: The Bank of England maintained its base rate at 5.25% in its November meeting, aiming to curb inflation without stifling economic growth.
- Fiscal Measures: The UK government’s energy subsidy programs and targeted financial support for low-income households have helped mitigate the impact of inflation on vulnerable groups.
Implications for Businesses and Consumers
- Household Budgets:
- Rising food and energy prices continue to strain household budgets, particularly for middle- and low-income families.
- Consumer spending on non-essential goods has shown signs of contraction as households prioritize necessities.
- Businesses:
- Retailers face the dual challenge of higher input costs and reduced consumer purchasing power.
- Service sector firms, particularly in hospitality, must navigate increased wage costs alongside price-sensitive customers.
- Housing Market:
- Higher mortgage rates, driven by elevated interest rates, have dampened housing demand and led to a cooling in property price growth.
Outlook for 2025
Looking ahead, the UK’s inflation trajectory will depend on several factors:
- Energy Market Stabilization: Expected regulatory changes and falling global energy prices may ease inflationary pressures.
- Wage Growth and Employment: Continued labor market strength will be crucial for sustaining consumer spending.
- Monetary Policy: The Bank of England’s decisions on interest rates will play a pivotal role in balancing inflation control with economic growth.
Conclusion
The consumer price inflation data for November 2024 highlights the complex interplay of global and domestic factors affecting the UK economy. While a slight moderation in inflation offers some relief, persistent pressures in energy and food prices underscore the challenges ahead. Policymakers, businesses, and households must navigate these dynamics carefully to ensure economic stability in the coming months.
By understanding these inflation trends and their implications, businesses can make informed decisions, and households can better manage their finances. For policymakers, this data reinforces the need for targeted interventions to address the root causes of inflation and support economic resilience.