The European Central Bank (ECB) announced pivotal monetary policy decisions on December 18, 2024, aimed at steering inflation towards its 2% medium-term target. These decisions, including a 25 basis point cut in the three key ECB interest rates, reflect updated assessments of inflation dynamics, economic recovery prospects, and financing conditions.
Key Highlights of ECB Decisions
1. Interest Rate Adjustments
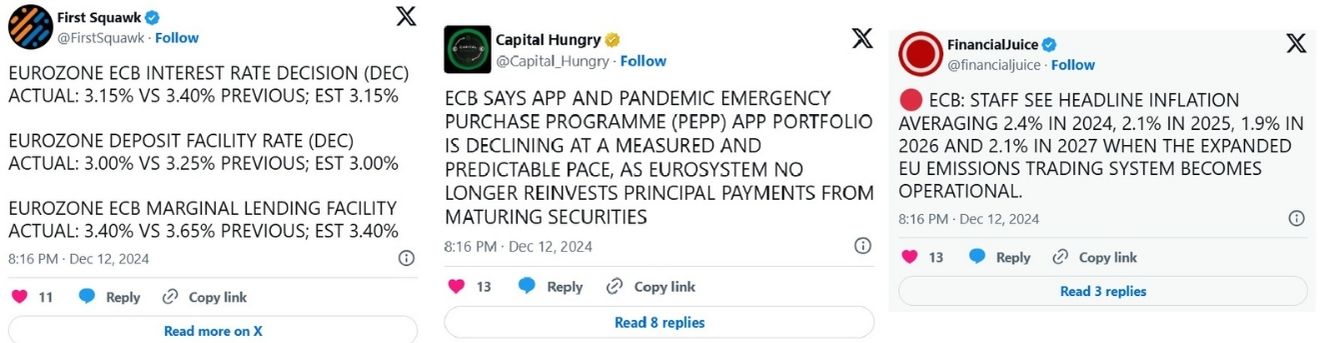
The ECB reduced the three key interest rates as follows:
- Deposit Facility Rate: Decreased to 3.00%
- Main Refinancing Operations Rate: Lowered to 3.15%
- Marginal Lending Facility Rate: Reduced to 3.40%
This decision, effective from December 18, 2024, reflects the ECB’s commitment to easing financing conditions while ensuring inflation stabilizes sustainably.
2. Inflation Outlook
The ECB’s updated projections indicate a steady disinflation trajectory:
- Headline Inflation: Expected to average 2.4% in 2024, 2.1% in 2025, and 1.9% in 2026, stabilizing around the 2% target.
- Core Inflation (excluding energy and food): Predicted at 2.9% in 2024, declining to 1.9% by 2026.
The gradual decline in inflation reflects easing domestic pressures, including wages and sectoral price adjustments.
3. Economic Growth Projections
Economic recovery is anticipated to progress at a slower pace than previously projected:
- Growth rates are forecast at 0.7% in 2024, 1.1% in 2025, and 1.4% in 2026.
- Real income growth and investment increases are expected to drive recovery, supported by the gradual easing of restrictive monetary policy.
Despite the recovery, tight financing conditions and the lingering effects of past interest rate hikes continue to weigh on economic activity.
Impact on Monetary Policy Instruments
Asset Purchase Programme (APP) and PEPP
- The ECB is reducing the PEPP portfolio by €7.5 billion monthly and will discontinue reinvestments by the end of 2024.
- The APP portfolio continues to decline predictably, aligning with the ECB’s balance sheet normalization efforts.
Refinancing Operations
The conclusion of targeted longer-term refinancing operations (TLTROs) marks a significant step in balance sheet adjustment. Banks will repay remaining borrowed amounts, reinforcing the ECB’s monetary policy strategy.
Analysis of ECB’s Approach
1. Data-Dependent Decision-Making
The Governing Council emphasizes a data-driven and meeting-by-meeting approach, focusing on:
- The inflation outlook based on incoming data.
- Dynamics of underlying inflation.
- The strength of monetary policy transmission.
This cautious approach ensures flexibility in responding to economic shifts without pre-committing to a fixed rate path.
2. Commitment to Price Stability
The ECB remains determined to stabilize inflation at 2%, utilizing all instruments within its mandate. The Transmission Protection Instrument further ensures the smooth functioning of monetary policy across euro area countries.
What This Means for the Eurozone Economy
- Lower Borrowing Costs: Eased financing conditions will benefit households and firms, fostering consumption and investment.
- Gradual Recovery: Economic recovery is expected to gain momentum, supported by fading effects of restrictive policies.
- Balanced Inflation Control: By addressing core inflation pressures, the ECB aims for a stable economic environment conducive to growth.
Conclusion
The ECB’s latest policy measures underscore its adaptability in managing inflation and supporting economic recovery. By balancing interest rate cuts with cautious asset purchase reductions, the ECB aims to ensure sustainable growth while adhering to its price stability mandate.
